Overview
NUMA (Non-uniform memory access) is a computer memory design used in multiprocessing, where the memory access time depends on the memory location relative to the processor.
Under NUMA, a processor can access its own local memory faster than non-local memory (memory local to another processor or memory shared between processors).
The benefits of NUMA are limited to particular workloads, notably on servers where the data are often associated strongly with certain tasks or users.
Configure NUMA topology on compute nodes that must support the topology. Nova instances will be pinned to dedicated CPU cores, which enables smarter scheduling and therefore improves guest performance.
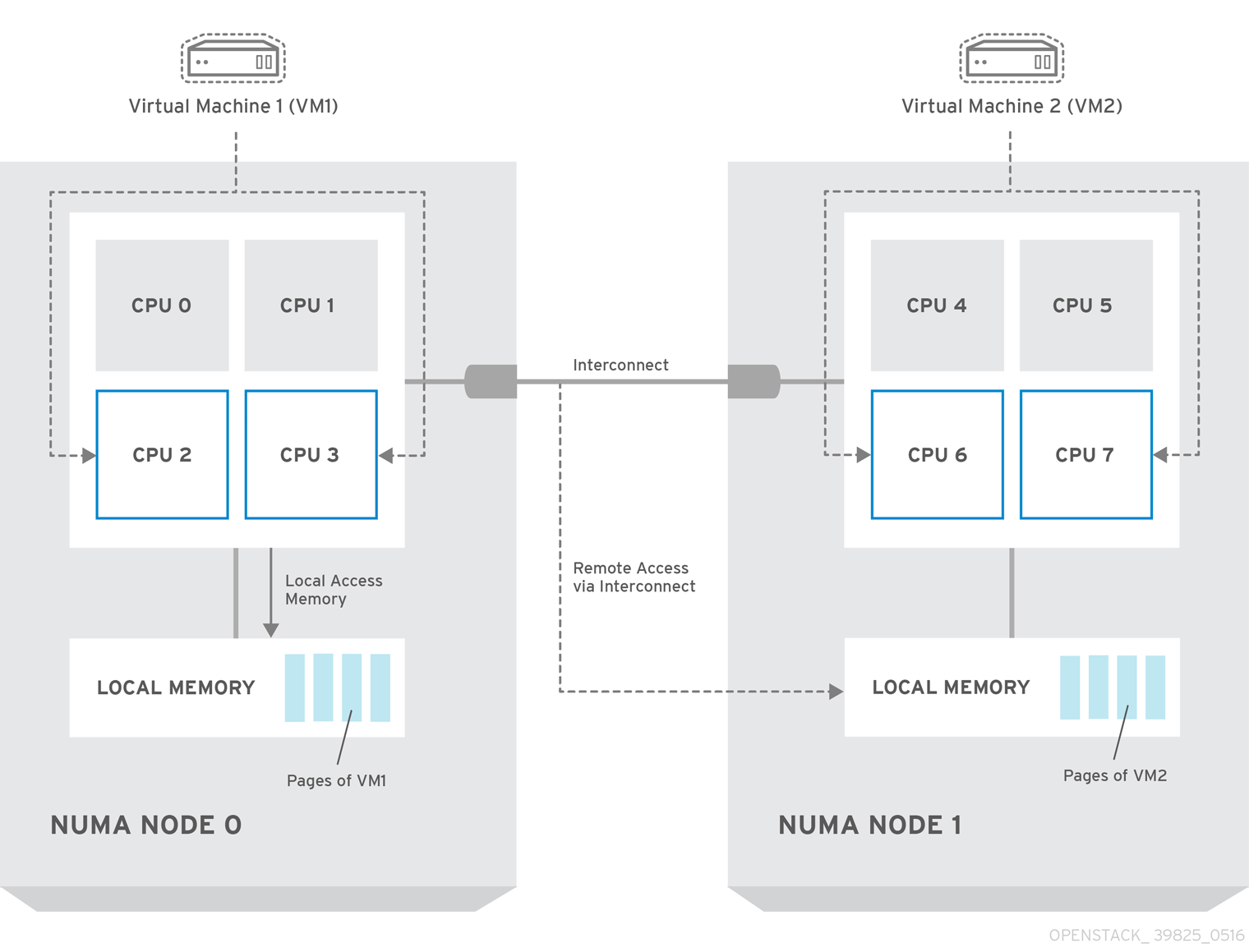
The above is an example of a two-node NUMA topology and the way the CPU cores and memory pages are made available.
Remote memory available via Interconnect is accessed only if VM1 from NUMA node 0 has a CPU core in NUMA node 1. In this case, the memory of NUMA node 1 will act as local for the third CPU core of VM1 (for example, if VM1 is allocated with CPU 4 in the diagram above), but at the same time, it will act as remote memory for the other CPU cores of the same VM.
Check the NUMA topology:
# lscpu | grep NUMA
NUMA node(s): 2
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-11,24-35
NUMA node1 CPU(s): 12-23,36-47
Check the memory access statistics of NUMA nodes:
# numastat -c
Per-node numastat info (in MBs):
Node 0 Node 1 Total
-------- -------- ---------
Numa_Hit 78064379 39901432 117965810
Numa_Miss 0 0 0
Numa_Foreign 0 0 0
Interleave_Hit 252 253 505
Local_Node 78064243 39901120 117965363
Other_Node 135 312 447
Configure Nova Compute
You must reserve some CPU cores across all the NUMA nodes for host processes and let the rest of the CPU cores handle your guest nova instances.
Set the vcpu_pin_set option in the /etc/nova/nova.conf file to the list of CPU cores reserved for guest processes:
vcpu_pin_set=8-47
Set the reserved_host_memory_mb to the amount of RAM to reserve for host processes:
reserved_host_memory_mb=8192
Restart the nova compute service.
Configure Nova Scheduler
add AggregateInstanceExtraSpecFilter and NUMATopologyFilter to the scheduler_default_filters option in /etc/nova/nova.conf.
Then restart nova scheduler service to reload the conf.
Set aggregate and flavor
Create an aggregate for the hosts that will receive pinning requests:
# nova aggregate-create cpu_pinning
+----+-------------+-------------------+-------+----------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata |
+----+-------------+-------------------+-------+----------+
| 4 | cpu_pinning | - | | |
+----+-------------+-------------------+-------+----------+
# nova aggregate-set-metadata 4 pinned=true
# nova aggregate-add-host cpu_pinning compute1
# nova aggregate-add-host cpu_pinning compute2
# nova aggregate-add-host cpu_pinning compute3
# nova aggregate-details 4
+----+-------------+-------------------+------------------------------------+---------------+
| Id | Name | Availability Zone | Hosts | Metadata |
+----+-------------+-------------------+--------------------- ------+---------------+
| 4 | cpu_pinning | - | 'compute1', 'compute2', 'compute3' | 'pinned=true' |
+----+-------------+-------------------+------------------------------------+---------------+
Create a flavor for the hosts that will receive pinning requests:
# nova flavor-create tiny.pin 10 512 1 1
Set the hw:cpu_policy specification of this flavor to dedicated to require dedicated resources, which enables CPU pinning:
# nova flavor-key 10 set hw:cpu_policy=dedicated
Set the aggregate_instance_extra_specs:pinned to true so as to ensure that instances based on this flavor have this specification in their aggregate metadata:
# nova flavor-key 10 set aggregate_instance_extra_specs:pinned=true
# nova flavor-show 10
+----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Property | Value |
+----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| OS-FLV-DISABLED:disabled | False |
| OS-FLV-EXT-DATA:ephemeral | 0 |
| disk | 1 |
| extra_specs | {"aggregate_instance_extra_specs:pinned": "true", "hw:cpu_policy": "dedicated"} |
| id | 10 |
| name | tiny.pin |
| os-flavor-access:is_public | True |
| ram | 512 |
| rxtx_factor | 1.0 |
| swap | |
| vcpus | 1 |
+----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Run nova boot --image image-id --flavor 10 server_name to boot an instance to verify your setting.
Check the instance libvirt xml configuration:
<numatune>
<memory mode="strict" nodeset="0"/>
<memnode cellid="0" mode="strict" nodeset="0"/>
</numatune>
<cputune>
<shares>1024</shares>
<emulatorpin cpuset="9"/>
<vcpupin vcpu="0" cpuset="9"/>
</cputune>
For libvirt xml details, refer to libvirt.xml
It’s possible fail to migrate an instance which has been configured to use CPU pinning.
